What is the Tuina?Tuina, also spelled Tui Na, is a form of Chinese therapeutic massage and one of the four main branches of Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), along with acupuncture, herbal medicine, and qigong. Tuina translates to "push and grasp" in Chinese, which reflects the primary techniques used in this therapy.Principles:What is the Sports Massage?Sports …
What is the Tuina?
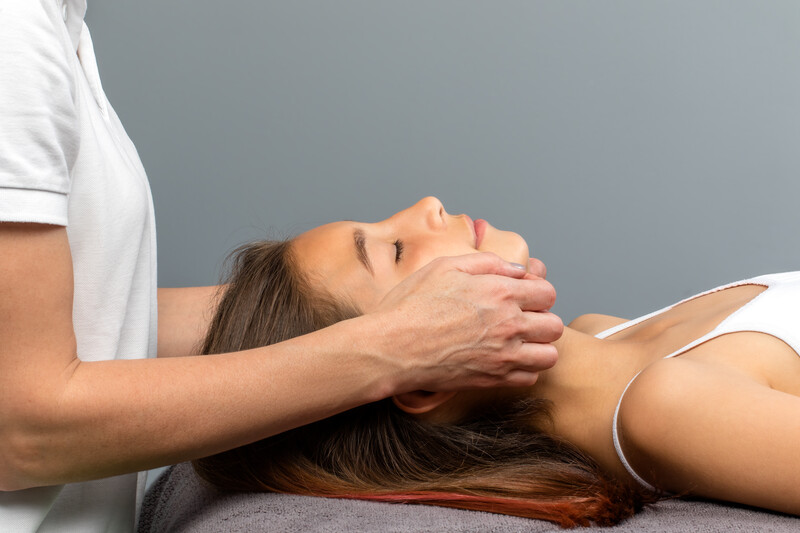
Tuina, also spelled Tui Na, is a form of Chinese therapeutic massage and one of the four main branches of Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), along with acupuncture, herbal medicine, and qigong. Tuina translates to “push and grasp” in Chinese, which reflects the primary techniques used in this therapy.
Principles:
- Based on TCM principles of balancing the body’s energy (Qi) flow.
- Utilizes the concept of meridians (energy channels) and acupressure points, similar to acupuncture.
What is the Sports Massage?
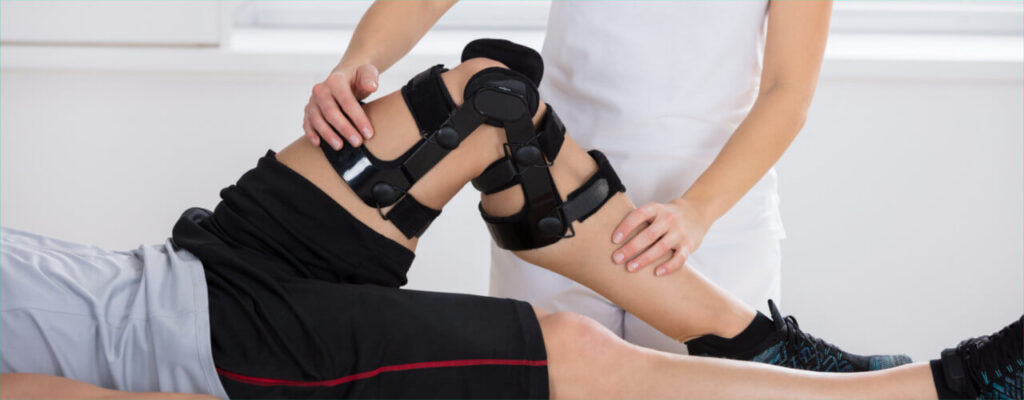
Sports massage is a specialized form of massage therapy designed to address the needs of athletes and physically active individuals. It involves the manipulation of soft tissues, including muscles, tendons, and ligaments, using a variety of techniques to enhance performance, prevent injuries, and promote recovery. Key elements of sports massage include:
1. Pre-event Massage: Aimed at warming up muscles and increasing flexibility before athletic events.
2. Post-event Massage: Focuses on reducing muscle soreness, promoting relaxation, and aiding recovery after physical exertion.
3. Maintenance Massage: Regular sessions to maintain optimal muscle condition, address minor issues before they become significant, and prevent injuries.
4. Rehabilitation Massage: Used to support the healing process and restore function after an injury.
Techniques used in sports massage can include deep tissue massage, stretching, friction, and trigger point therapy, tailored to the specific needs of the individual.
Who needs the Sports Massage?
Sports massage is beneficial for a wide range of individuals, not just athletes. Here are some groups who might benefit from sports massage:
1. Professional Athletes: To maintain peak performance, prevent injuries, and recover quickly.
2. Recreational Athletes: For improving performance, reducing the risk of injury, and aiding in recovery.
3. Fitness Enthusiasts: To help manage muscle soreness and maintain flexibility.
4. People with Physically Demanding Jobs: Those who engage in heavy lifting or repetitive physical tasks can benefit from reduced muscle tension and pain relief.
5. Individuals Recovering from Injuries: To aid in the rehabilitation process by improving flexibility and reducing pain.
6. Older Adults: To help maintain muscle function and flexibility.
7. Anyone Experiencing Muscle Pain or Tension: For general muscle relief and improved circulation.
Why to need the Sports Massage?
Sports massage offers several benefits, particularly for athletes and physically active individuals:
1. Injury Prevention: It helps to identify and address potential issues before they develop into injuries.
2. Enhanced Performance: By improving flexibility and reducing muscle tension, it can enhance athletic performance.
3. Faster Recovery: It aids in faster recovery post-exercise by reducing muscle soreness and promoting blood flow.
4. Pain Relief: It can alleviate pain from chronic conditions or specific injuries.
5. Improved Circulation: It enhances blood and lymphatic circulation, which helps in the removal of metabolic waste products.
6. Mental Relaxation: It reduces stress and promotes relaxation, which can improve focus and mental clarity.
Overall, sports massage is a valuable tool for maintaining optimal physical condition and performance.
Summary:
While both Tuina and sports massage aim to alleviate pain and promote healing, they differ significantly in their origins, techniques, and goals. Tuina is a holistic practice rooted in Traditional Chinese Medicine that focuses on balancing the body’s energy, while sports massage is a Western technique focused on the physical needs of athletes, enhancing performance, and facilitating recovery.